INCREASE MACHINE PRODUCTIVITY WITH PHASE-SHIFTING DIFFERENTIAL GEARBOXES
Differential gearboxes control rotary position and speed
Are you considering differential gearbox technology as a possible solution to your next rotary motion control application? Differential gearboxes are used in a number of automated manufacturing applications to provide static and dynamic rotary motion control. These gearboxes are often referred to as phase-shifting differential gearboxes due to their ability to adjust the phase or angular position of the output shaft relative to the input shaft providing mechanical or electro-mechanical rotary motion control for virtually any type of rotating manufacturing process. The differential action or phase adjustment occurs when a manual or motorized rotation is applied to a third shaft, typically referred to as the control shaft. What does this mean to a design engineer or end user? The ability to control the position or speed of rotating processes results in increased machine productivity, because there’s less downtime, less material waste, and higher product quality.

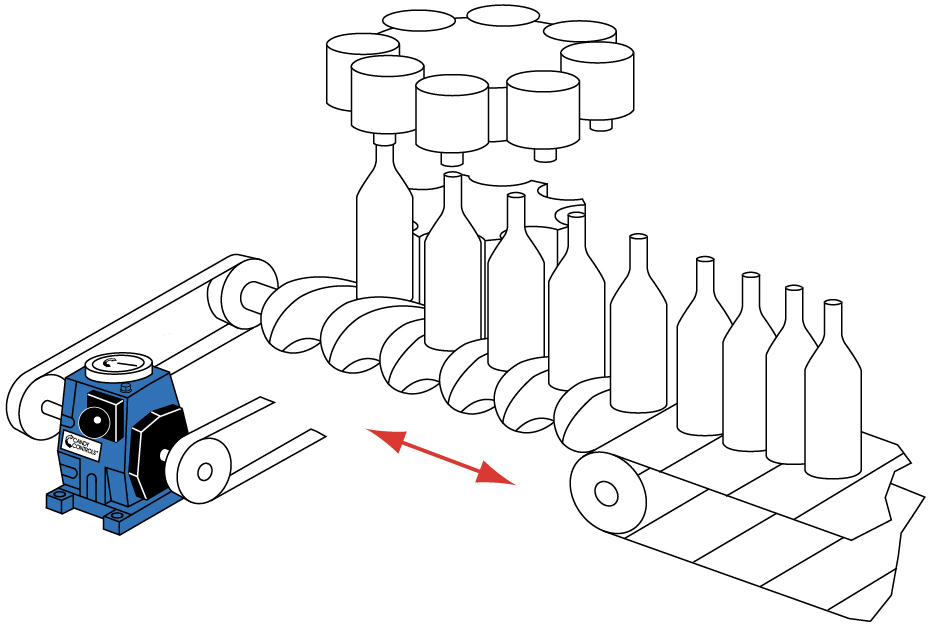
Position food, beverage and pharmaceutical containers for forming filling and sealing applications.
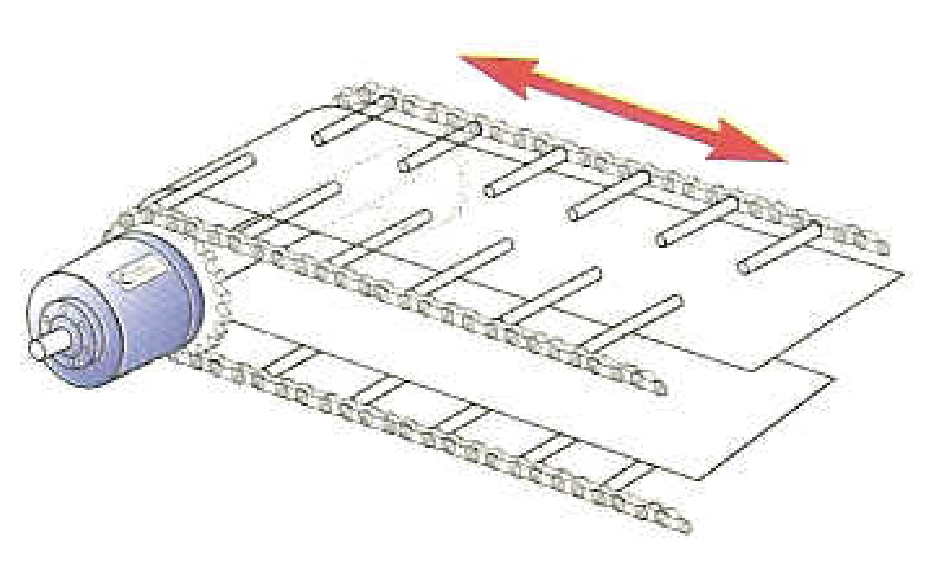
Adjust lug or flight positions for various folding and cartoning applications.
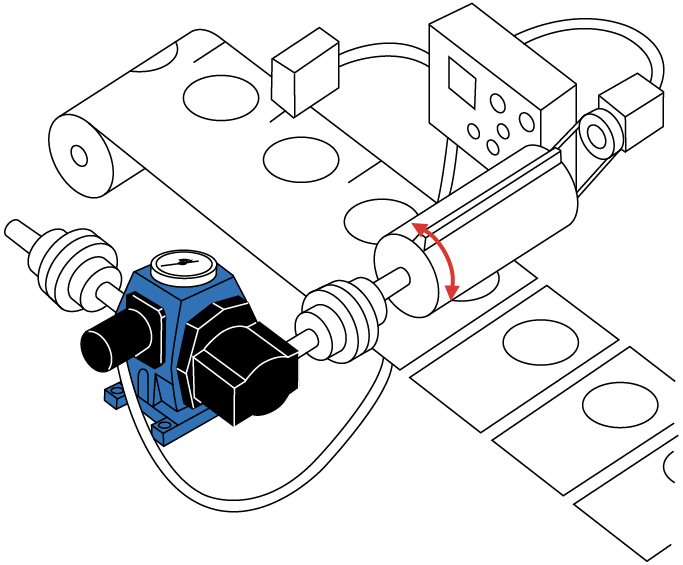
Register printing, perforating and die cutting cylinders with open or closed loop control systems.
Different gearboxes for different drivetrains
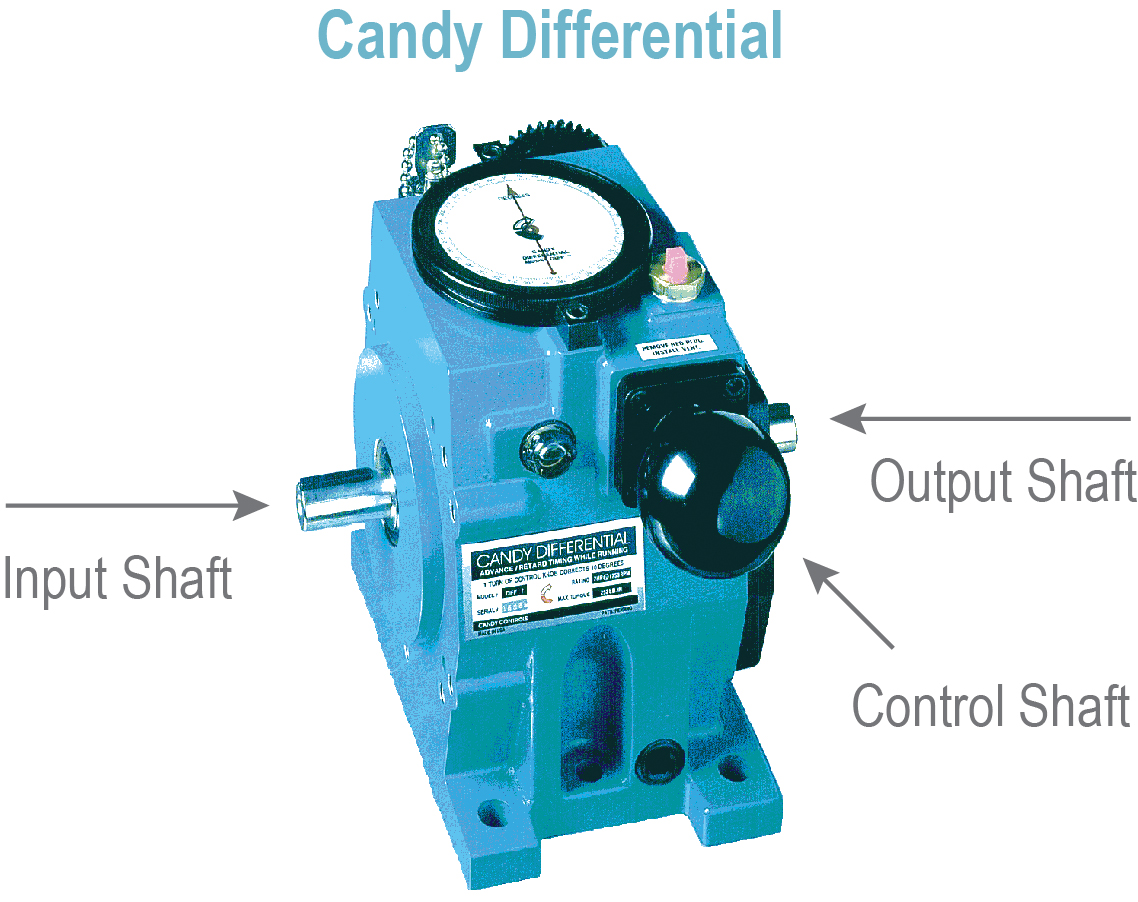
Phase-shifting gearboxes are available in a number of different sizes, configurations, and ratios, including both foot mounted and shaft mounted designs. Regardless of whether they are in line, right angled, foot mounted, shaft-mounted, 1:1, or otherwise, these gearboxes allow the user to adjust the position and/or speed of the output shaft and the process its driving independent of the input. This adjustment can be accomplished while the machine is running or stopped during setups and changeovers. In most cases, a machine’s drivetrain design determines which type of differential gearbox configuration and ratio fits it best.
Machines with a traditional line shaft, for instance, might use a right angle phase shifting gearbox inserted into the line shaft. In this case, the output shaft is able to control the position or speed of whatever machine section or process it’s driving, independent of other sections or processes powered from the line shaft. On the other hand, machines that use gears or timing belt pulleys to transfer power along the side frame, which drives various processes along the way, might incorporate a shaft-mounted differential with the input/output gear or pulley mounted to its outer housing.
What kind of machines and applications are these gearboxes used on? Virtually any type of rotary manufacturing process can use a phase-shifting differential gearbox to improve machine productivity. Below are examples of applications that have benefited from the capabilities of phase-shifting gearboxes.
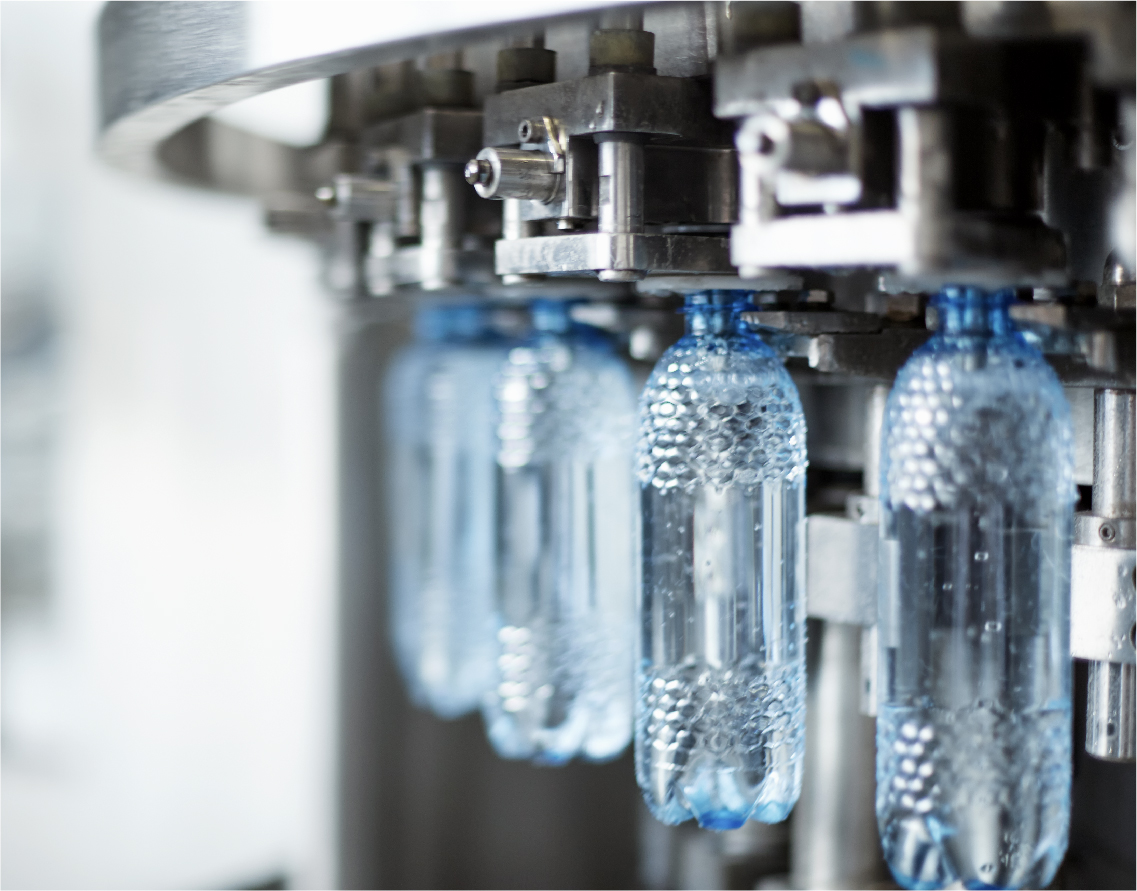

Food and Beverage Processing
Many food processing machines have rotary assemblies that can be timed by a phase-shifting gearbox. Conveyor belts or chains with flights that hold and position food trays as they pass under dispensers are driven by rotating pulleys or sprockets that can be timed/controlled. Screw driven filling machines can use differentials to advance and reverse the position of the screw, thus controlling the position of a bottle underneath a filling head.
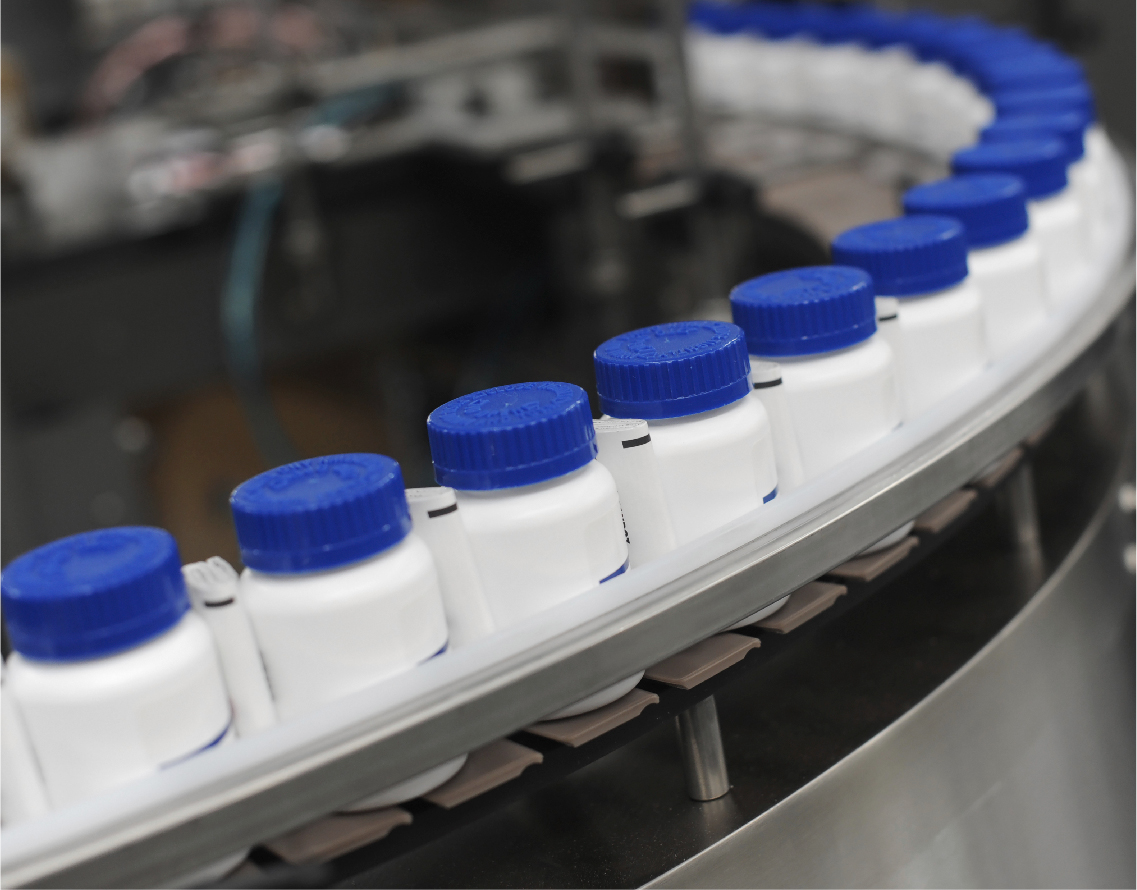

Packaging
Carton packaging machines and other packaging equipment have rotary motion control needs. Cartons or boxes and their tabs are often manipulated by rotating components, and rotating pusher heads are commonly used to push product into erected cartons. Food packaging equipment often uses rotating cylinders to seal and cut pre-printed packaging material around the product for applications like candy bars or small packets of sugar. Because the packaging material is preprinted, it needs to be positioned correctly relative to the product, often involving a rotary process.
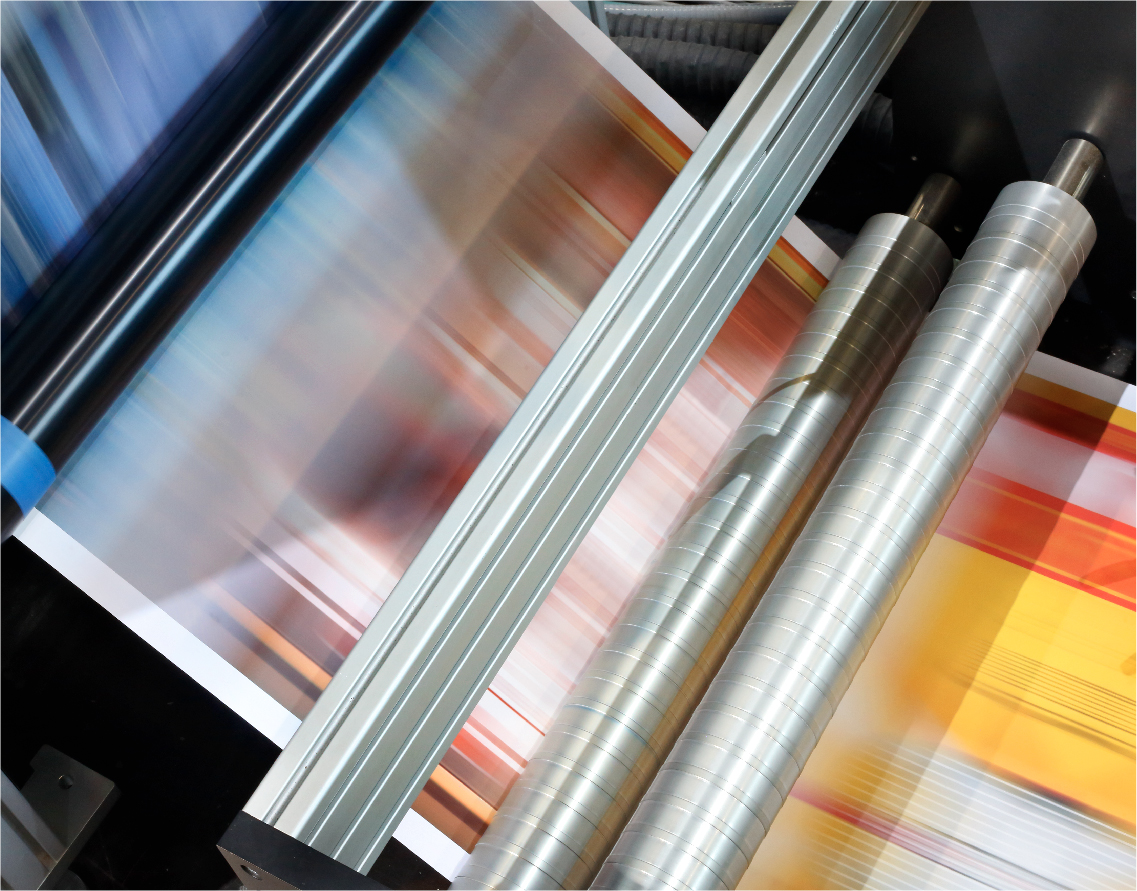

Web Printing and Converting
Web printing and converting machines incorporate rotating printing, die cutting, and tensioning cylinders. Phase shifting differential gearboxes can be used for print-to-print and cut-to-print register control, as well as web tension and draw control, ensuring that colors are applied correctly and cuts are made in the right location(s).
Are you thinking, “Sounds like I could use a servo system to do those things”?
Yes, servo motors have replaced differential gearboxes in a number of applications. However, phase shifting differential gearboxes still have some advantages, perhaps the largest of which is simplicity. Differentials are mechanical gearboxes; they have an input shaft, an output shaft, and a control shaft. They are simple enough to understand, easy to install, especially in the case of a machine retrofit, and they are much easier to maintain and troubleshoot compared to a servo system. Not all companies can afford to employ the electrical or control systems engineers necessary to program and maintain servo systems. These companies can still enjoy the benefits of controlled motion with a differential gearbox.
Differentials may offer the best solution for machine retrofits from both a cost and risk perspective. Differential retrofits typically do not require significant changes to the drivetrain, which often occurs when installing direct drive servo systems. Phase shifting differentials might also present the best solution for the end user who prefers a mechanical drivetrain and generally a lower cost production machine due to both a lower up front purchase price and lower ongoing maintenance costs.
When presented with the need to control rotary position and speed, it’s wise to weigh the pros and cons of all viable motion control solutions, including phase shifting differentials. Candy Controls has 60 years of experience helping OEM and MRO customers improve machine productivity through the implementation of differential gearbox technology.
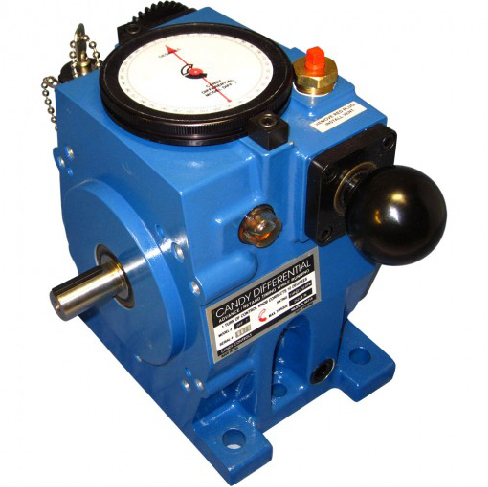
Candy Differential
- Precise rotary motion control gearbox
- Dynamic, bi-directional position control
- 1:1 counter rotating I/O shafts
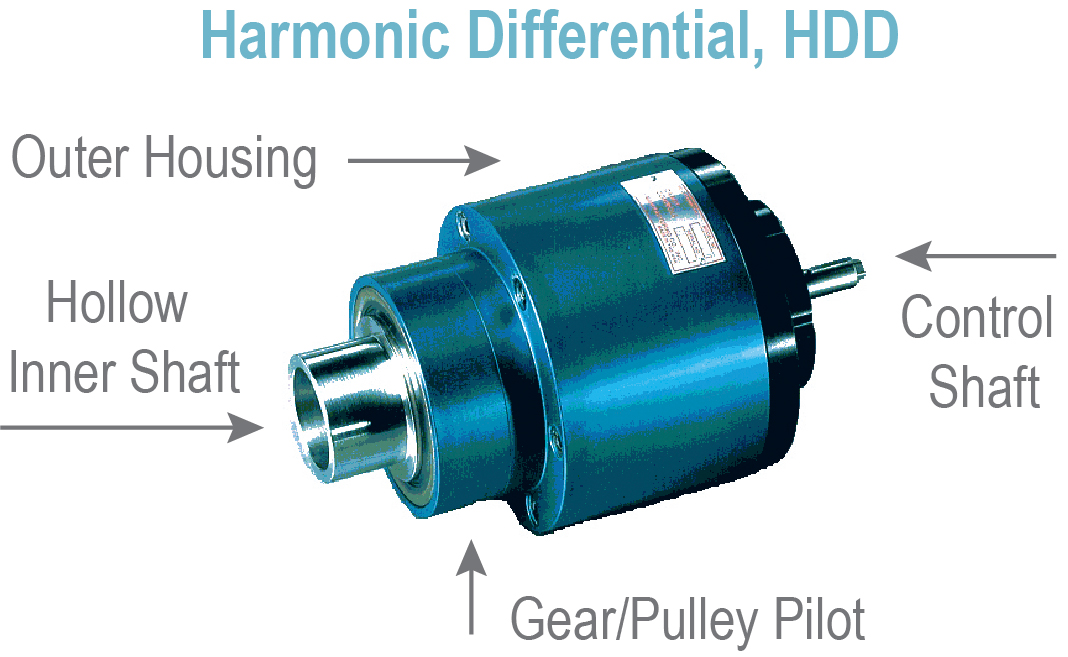
Candy Harmonic Differential, HDD
- Precise position control and speed trimming
- Shaft-mounted, 1:1 phase shifting gearbox
- Compact, low backlash design
Dynamic Differential
- Phase-shifting gearbox
- Infinitely adjustable while running
- 1:1 counter rotating I/O shafts
Candy Harmonic Differential, HDC
- Position and speed trimming gearbox
- ½%-2% built-in gain or draw
- Zero backlash, shaft-mounted design
 Candy Controls
Candy Controls





